A large part of the British population has suffered, suffers or will suffer from back pain and this, at an increasingly young age! A bad position at work, an inappropriate effort or a peak of stress can cause lower back pain. In this article we will give some postural advice to say goodbye to your back pain.
There are some simple healthy hygiene rules that you need to impose on your spine on a daily basis. Knowing the mechanics of the back to know how to take care of it, watching one’s weight, practicing regular physical exercises and fighting stress through relaxation will help reduce back pain.
Anatomy of the Spine: 33 vertebrae and 244 muscles
The human spine is the central part of the skeleton. It is also known as scaffolding of the entire body. The spine supports the head, anchors the muscles and ribs, allows standing, absorbs shocks and protects the spinal cord, which transmits the nerves between the brain and the rest of the body. The spine provides structural support to the body that allows us to stand straight. About half of the body’s weight is supported by the spine.
The average person consist of 33 vertebrae, stacked one on top of the other and separated by inter-vertebral discs, which are cushioning cartilage pads. The spine is not straight. It is curved to compensate for the stresses created by standing and acts as a spring to support gravity and shock waves. 244 muscles, symmetrically distributed on both sides of the spine, ensure the stability of the trunk and control the body’s posture.
Correct Posture
Choosing the right posture from the outset is the best way to ensure that your back is in good condition. Right posture means that the pressure on the spine is evenly distributed between the joints. With relaxed muscles, the spine should be slightly curved, neither straight nor too arched.
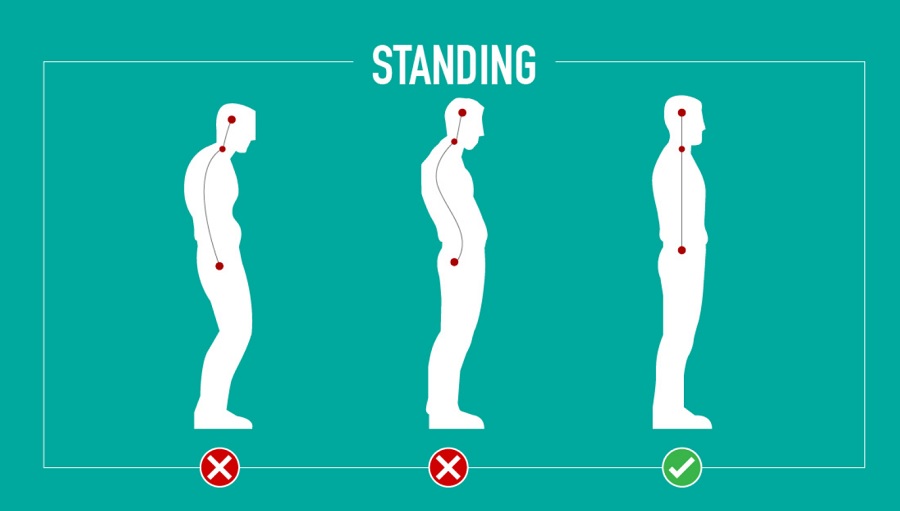
Right Standing Posture
Stand with your head upright, neck extended and vertical, shoulders horizontal and relaxed, stomach and buttocks tucked in to support the spine, pelvis slightly tilted back, knees fairly flexible and toes flat. Distribute your body weight evenly over your feet.
Right Sitting Posture
When sitting on chair, place yourself at the back with your weight distributed over your buttocks and thighs, parallel to the floor and forming a right angle with your calves. If necessary, support the back with a small cushion. The shoulders should be low, thrown back and relaxed. Do not lean your head forward. To keep your back straight, tighten your stomach.

Read also: Best Office Chair for Sciatica
Right Posture at the Office
The ideal position for people with weak lumbar and pelvic muscles is to use a chair that is tilted downwards by 5° so that the weight of the body is shifted from the hips to the thighs and from the knees to the floor. At the office, work preferably on an inclined surface, such as a drawing board. Change your position often. Do not wedge the telephone between your ear and shoulder, as this strains the neck muscles. Compensate for the static position by stretching in the morning and walk home.
Exercise
It is necessary to start by releasing muscle tension in order to reduce contracture. Then, move and relax, i.e. exercise to regain optimal mobility (swimming, walking, cycling). Once mobility has been regained, it is a good idea to build up muscles and try to maintain a good muscular balance.
If you haven’t exercised for a long time, you should have a check-up with your doctor before you start exercising again. And if you feel any pain when you start again, report it to your doctor. Don’t rush into it, take your time, listen to your body. Stretch it out, move around, and above all, forget the notion of performance. Simply enjoy the pleasure of being in top shape. Progress by stages, you will save time.
Never do any exercise or sports activities without warmup. This applies to a golf swing, a tennis backhand, a ball kick, a ski run or a game of pool! It is no coincidence that professional sportsmen and women train daily and carry out stretching and warm-up exercises before any competition. Remember the suspension exercise to relieve muscular and articular tension momentarily.
Forward Bend Stretch
Relax your back by tilting your chest forward, “letting go” completely. Standing, tilt your torso forward, relaxing completely for 10 seconds while exhaling slowly through your mouth. Stand up, unwinding each vertebra while breathing in through your nose. Practice this position 3 times in a row.
Upward Stretch
Stretch your arms upwards as far as possible for 10 seconds, breathing out slowly through your mouth. Then release your arms completely downwards by breathing in through your nose for 8 seconds. Rest your heels on the floor as you release. Or hang from a bar attached to the doorposts to relax the inter-vertebral discs and the static and postural muscles.
Watch your Weight
Being overweight has a negative effect on the back, particularly the load placed on the hip and lumbar joints. It requires more effort and accelerates wear and tear on the joints, leading to the early onset of osteoarthritis and making the back vulnerable (back pain and disc problems). In men, since the weight is located on the stomach, the muscles of the abdominal belt are less supportive of the spine when relaxed. Women with large breasts tend to bend forward and by correcting their posture, back pain can be reduced.
Read also: 7 Reasons Exercising For Weight Loss Fails
A Right mattress for your Spine
A good mattress should be firm, but at the same time it should follow the contour of the hips and shoulders, thus supporting the spine without distorting it. Try it out for a while in the shop. If your partner has a big weight difference with you, take two mattresses. The pillow should also be adapted to the sleeping position and to the support of the head. Whatever position you lie in, your neck should remain in line with your spine so that your muscles can relax.
